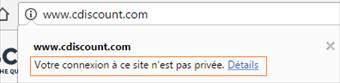
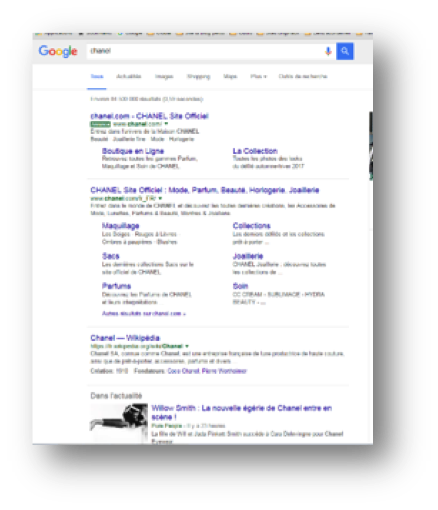
Between Mars, 2016 and Mars, 2017, Let’s Encrypt has issued 15 270 SSL certificates containing “PayPal” term, 14 766 of these certificates were issued for domains leading to phishing websites. It’s the result of the recent analysis led by Vincent Lynch, SSL expert.
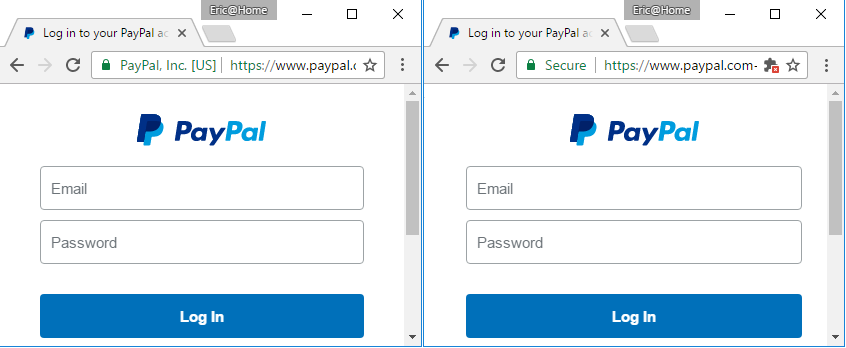
Lynch was closely interested in this case, after an interesting article published by Eric Lawrence (Google Chrome Security Team) in January 2017, the image above is from this article named “Certified Malice “which exposes deceitful SSL certificates and counts “only” 709 cases for PayPal and much more for big American brands: BankOfAmerica, Apple, Amazon, American Express, Chase Bank, Microsoft, Google…
What’s the impact on web users?
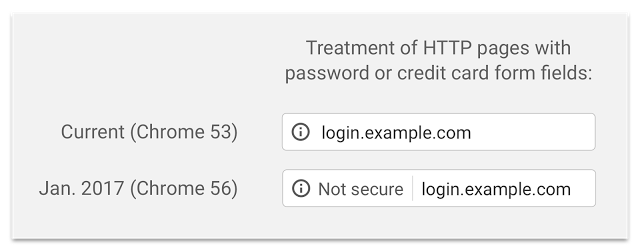
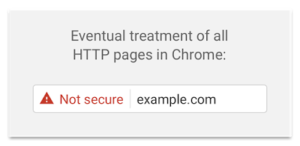
In January 2017, Google and Mozilla have updated their browser with Chrome 56 and Firefox 51, and a major change has appeared for web users: “Secure” and “Not secure” have appeared in the address bar.
In 2015, the initiative Let’s Encrypt, supported by big names of Internet (EFF, Mozilla, Cisco, Akamaï…) was created with the purpose of massively and freely spreading SSL certificates to the whole world. One year and a half later, Let’s Encrypt issued millions of certificates and other initiatives have followed.
Who says free, says few or no verification for delivering certificates, and an army of cybercriminals who rush towards these certificates to secure their illicit contents: phishing, malware… and show the term “secure” on their address bar. How can the random web user easily differentiate between real and fake?
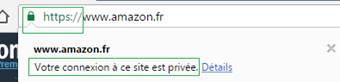
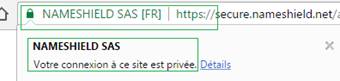
For reminder, there are three verification levels for certificates allowing to show HTTPS: Domain Validation (DV) considered as low authentication, Organization Validation (OV) with high authentication and Extended Validation (EV) with strengthened authentication.
Free certificates are DV, and represent almost 90% of certificates, most of the time on “small” websites. OV certificates (9%) and EV certificates (1%) are fewer but protect almost all websites with high traffic. GAFA (Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon), are all in OV or EV for example.

The problem for web user is the lack of distinction in browsers between DV and OV certificates. These two types are shown the same way, as being “secure”, but EV certificates display the name of the certificate’s owner in the address bar.
By looking at the image at the beginning of this article, we understand easily the concern on EV for PayPal: to easily differentiate real from fake. This is the reason why Nameshield will systematically advise the use of EV for display website, in particular for their clients exposed to cybersquatting, phishing or counterfeit.
Two forces opposed for the future of HTTPS
Sadly, things aren’t so simple, and where logic would like to differentiate clearly between the three types of certificates, or at least two types (DV/OV), Google disagrees and wishes, on the contrary, to suppress the EV display altogether. Chris Palmer (Senior Software Engineer for Chrome) subtly confirms this point in his article published here.
Today we are in a situation where Historical Certification Authorities, Microsoft and to a smaller extent, Apple, are facing Google, Mozilla and Let’s Encrypt in a perspective resumed here:
| Google/Mozilla/Let’s Encrypt perspective:
HTTP = not secure
HTTPS = secure |
Historical Certification Authorities/ Microsoft/Apple perspective:
HTTP = not secure
HTTPS DV = no sign in the address bar
HTTPS OV = secure
HTTPS EV = company’s name in the address bar |
Inside the higher authority of SSL, the CAB/Forum, the discussion is still opened at this moment. We can easily understand that Certification Authorities look unfavorably at the end of the visual distinction between DV/OV/EV in browsers, it’s their purpose to deliver certificates with high authentication, but is it wrong? It’s to reassure the web users by securing the identity of the website they visit.
In the opposite, Google and Let’s Encrypt don’t hesitate to say that phishing and guarantee of website content, don’t depend on Certification Authorities, and that there are other systems responsible for that (for example, Google Safe Browsing). Therefore we have to have a binary perspective: exchanges are encrypted and inviolable (= HTTPS = secure) or they aren’t (= HTTP = not secure). We can simply wonder by this perspective, which defends itself, if it’s not a semantic problem of the used term “secure” instead.
What does “secure” mean for web users? By seeing “secure” in their address bar, do they enter their login/password or credit card numbers? We can think that yes, they do, and in this case, actual risk does exist. Kirk Hall (Director Policy and Compliance – SSL, Entrust) has done a noticed intervention at the last RSA conference on this subject (if you have time, the record is here).
You can’t neglect financial industry weight and big companies which look unfavorably at the growth of fraud online risk, Google can’t ignore that.
How to reassure web users?
For the time being, we can only encourage you to choose Extended Validation certificates for your display websites and/or your e-shop in order to facilitate web users’ tasks and to stay informed of what’s going on on the web. To reassure and educate web users by mentioning on your website the choice you have made in security and authentication.
As you probably monitor domain name registrations on your brands, today you can also monitor certificates registrations so you can react quickly.
And as web user, when the term “secure” is mentioned in the address bar, systematically control the certificate’s details to see who the owner is.








 Chrome 53 launched on 31 August 2016 and with it Google is continuing its offensive for a safer internet.
Chrome 53 launched on 31 August 2016 and with it Google is continuing its offensive for a safer internet.